随着细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4和6(CDK 4/6)抑制剂的问世,激素受体阳性乳腺癌的治疗被彻底改变。不过,CDK4/6抑制剂一线治疗的肿瘤客观缓解率不到50%,而且几乎全部一开始有效的患者在治疗期间都产生耐药,随后死亡。因此,有必要对CDK4/6抑制剂治疗乳腺癌的有效性和耐药性进行预测,避免浪费金钱、时间和生命。
2024年3月5日,英国《自然》旗下《自然癌症》在线发表美国圣迭戈加利福尼亚大学的研究报告,利用人工智能可视化神经网络建立肿瘤细胞结构深度学习模型,对CDK4/6抑制剂哌柏西利的有效性和耐药性进行多组学大数据分析。
为了阐明潜在机制,该研究首先根据718个癌基因、131个癌基因编码蛋白质组件层次结构参考图谱、1244个基因组特征肿瘤细胞系药物疗效数据,构建出可解释的深度学习模型,用于分析哌柏西利的疗效。这些数据包括哌柏西利的疗效及其在947个细胞系中的特征。为了进行基准检验比较,该研究还在至少200个细胞系中研究分析了50种非CDK相关药物,这些药物的细胞反应显示出足够的变异性,并有许多敏感和耐药的病例。
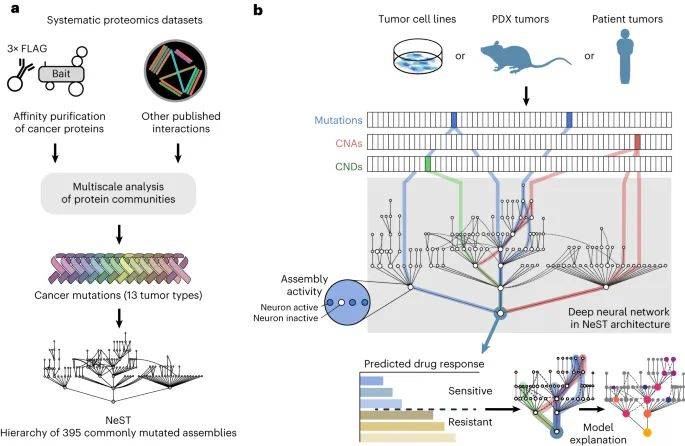
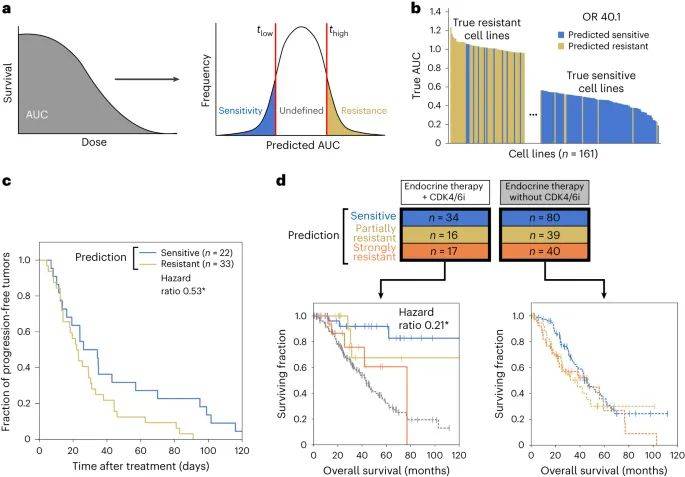
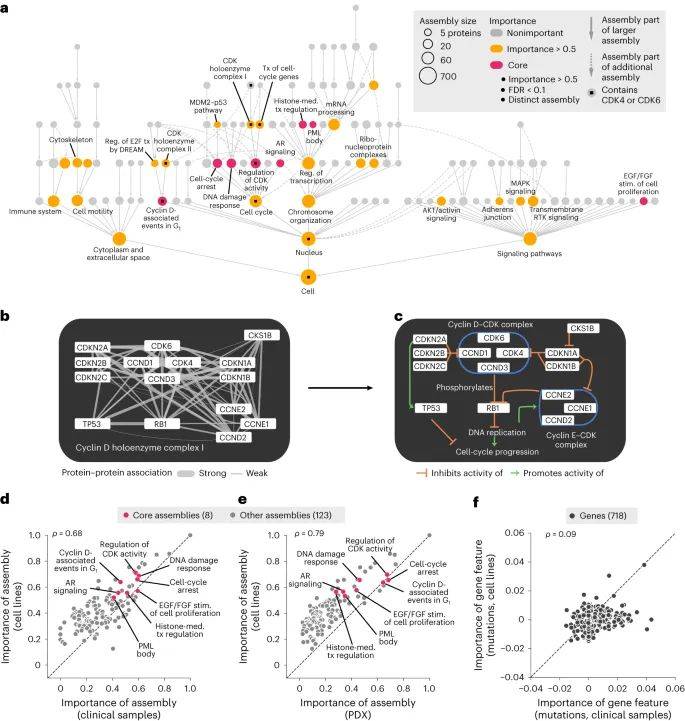
随后,该模型确定8个核心组件,整合了90个基因罕见和常见的改变,可以对哌柏西利敏感和哌柏西利耐药细胞系进行分层。这些多基因生物标志物能够预测哌柏西利对患者和患者来源异种移植物的疗效,而单基因生物标志物则不能。
大多数预测疗效的蛋白质组件可以通过基因编辑技术破坏而调节哌柏西利疗效。经过验证的组件与细胞周期控制、生长因子信号传导和组蛋白调节复合物相关,该复合物通过激活组蛋白赖氨酸乙酰转移酶KAT6A和转导蛋白β样1X受体TBL1XR1以及转录因子RUNX1促进细胞周期从DNA合成前期进入DNA合成期。
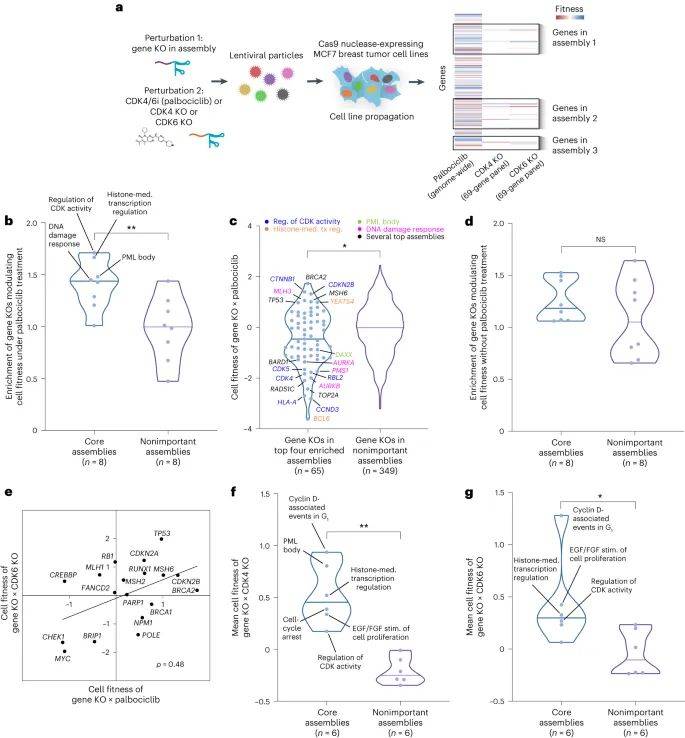
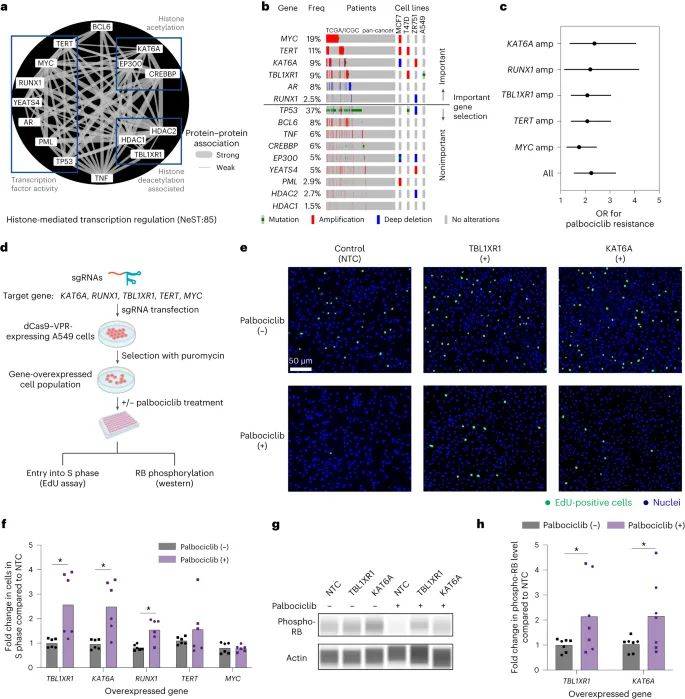
因此,该研究结果表明,根据肿瘤基因谱进行人工智能深度学习综合分析,能够预测哌柏西利对乳腺癌的有效性和耐药性。
Nat Cancer. 2024 Mar 5. IF: 22.7
A deep learning model of tumor cell architecture elucidates response and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors.
Sungjoon Park, Erica Silva, Akshat Singhal, Marcus R. Kelly, Kate Licon, Isabella Panagiotou, Catalina Fogg, Samson Fong, John J. Y. Lee, Xiaoyu Zhao, Robin Bachelder, Barbara A. Parker, Kay T. Yeung, Trey Ideker.
University of California, San Diego, CA, USA.
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors (CDK4/6is) have revolutionized breast cancer therapy. However, <50% of patients have an objective response, and nearly all patients develop resistance during therapy. To elucidate the underlying mechanisms, we constructed an interpretable deep learning model of the response to palbociclib, a CDK4/6i, based on a reference map of multiprotein assemblies in cancer. The model identifies eight core assemblies that integrate rare and common alterations across 90 genes to stratify palbociclib-sensitive versus palbociclib-resistant cell lines. Predictions translate to patients and patient-derived xenografts, whereas single-gene biomarkers do not. Most predictive assemblies can be shown by CRISPR-Cas9 genetic disruption to regulate the CDK4/6i response. Validated assemblies relate to cell-cycle control, growth factor signaling and a histone regulatory complex that we show promotes S-phase entry through the activation of the histone modifiers KAT6A and TBL1XR1 and the transcription factor RUNX1. This study enables an integrated assessment of how a tumor's genetic profile modulates CDK4/6i resistance.
DOI: 10.1038/s43018-024-00740-1
原文共享

来源|SIBCS
排版编辑:肿瘤资讯-Astrid











 苏公网安备32059002004080号
苏公网安备32059002004080号


