为提升乳腺癌诊疗水平,促进与国际乳腺癌领域专家交流,打造碰撞理念的中青年学术交流平台,“愈见新力量-乳腺癌中青年专家国际交流学院”系列栏目自隆重推出广受关注。本栏目着眼于乳腺癌诊疗的热点难点问题,讨论交流最新的研究进展和临床经验,激发新的学术思维。本期会议特邀美国华盛顿大学医学系血液肿瘤学部主任Sara A. Hurvitz教授参与,汇聚国内多位乳腺癌中青年专家,共同聚焦转移性乳腺癌(MBC),特别是脑转移患者的治疗策略和发展方向。

HER2+晚期乳腺癌的治疗策略和进展
Treatment strategies and progress of HER2+ advanced breast cancer
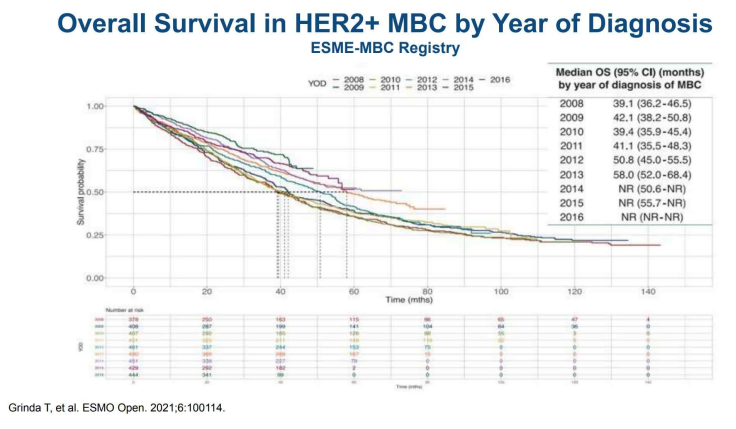
Sara A. Hurvitz教授介绍了以HER2为靶点的药物研发。HER2阳性(HER2+)MBC患者的治疗,使中位总生存(OS)在近年间从39.1个月增加至58个月,但HER2阴性及三阴性MBC的OS基本没有改善,仅维持在1年左右。
Professor Sara A. Hurvitz presented the development of drugs targeting HER2, which has changed the natural history of HER2-positive (HER2+) MBC, leading to an increase in the median overall survival (OS) from 39.1 months to 58 months in recent years. However, The OS of HER2-negative and triple-negative MBC has basically not improved and only remains at about 1 year.
HER2+MBC的一、二、三线治疗方案
First, second and third-line therapies for HER2+ MBC
一线标准治疗方案是帕妥珠单抗联合曲妥珠单抗,并辅以基于紫杉醇的化疗,这一方案是基于2012年发表的CLEOPATRA研究结果。鉴于DESTINY-Breast03研究中报告的显著的无进展生存期(PFS)和总生存期(OS)的改善,预计DESTINY-Breast09一线治疗研究将取得积极结果,这可能会使T-DXd成为新的一线治疗标准。然而,考虑到与T-DXd相关的副作用,如恶心、腹泻和中性粒细胞减少,注意患者的生活质量显得非常重要。而在耐受性方面,长期使用HP双靶维持治疗可能更为理想。
二线标准治疗一直是第一代抗体药物偶联物(ADC)T-DM1。直到近期,随着DESTINY-Breast03研究结果的发布,T-DM1被新一代ADC药物T-DXd所取代。另一种可用的二线治疗方案是酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(TKI)图卡替尼,它对HER2具有高度特异性,并且能够穿透血脑屏障。与其它TKI如奈拉替尼和吡咯替尼相比,图卡替尼引起的副作用较少,如腹泻。在二线治疗中,将其与T-DM1联合使用,与单独使用T-DM1相比,可以提高PFS。然而,其OS数据尚未成熟,仍在持续随访中。对于没有脑转移的MBC,更倾向于选择T-DXd作为二线治疗方案。
至于三线治疗,可选的方案包括图卡替尼联合曲妥珠单抗以及卡培他滨,或者是T-DM1。
The first-line standard care is pertuzumab + trastuzumab combined with taxane-based chemotherapy, which is based on the results of the CLEOPATRA study published in 2012.
Until recently, the standard second-line therapy was the first generation antibody drug conjugate (ADC), T-DM1. With the results of DESTINY-Breast03, T-DM1 was replaced with a next-generation ADC, T-DXd. Given the impressive progression free survival and overall survival reported in that study, it is anticipated that the DESTINY-Breast09 first-line study will be positive, leading to T-DXd becoming a standard front-line option. However, of the side effects associated with T-DXd, such as nausea, diarrhea, and neutropenia, it will be important to pay attention to the patient's quality of life as it may be that maintenance HP is better tolerated long term. Another second line therapy available is the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), tucatinib, which is highly specific for HER2 and can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. It has fewer side effects such as diarrhea than other TKIs, like neratinib and pyrotinib, and when added to T-DM1 in the second line, it is associated with an improved PFS compared to T-DM1 alone. However, OS data are not yet mature and are under continued follow-up. For MBC without brain metastases, Professor Hurvitz prefers to choose T-DXd as the second-line treatment.
Third-line treatment options include , tucatinib + trastuzumab combined with capecitabine, or T-DM1.
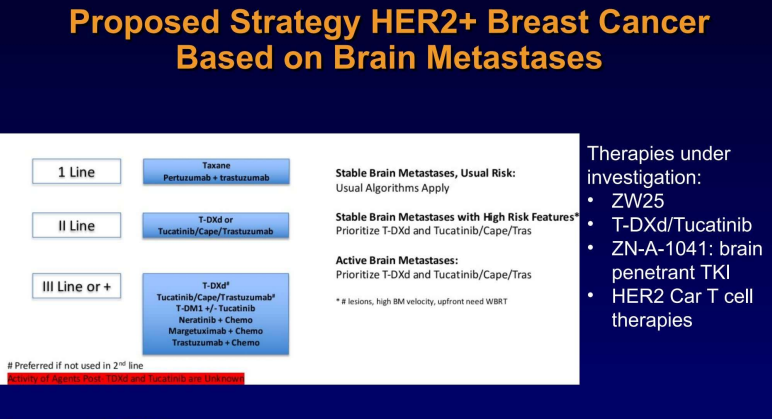
HER2+MBC脑转移的治疗推荐
Treatment recommendations for HER2+ MBC brain metastases
HER2+MBC患者中,脑转移的发生率随着治疗线数的延长而增加。目前,对于无症状的患者,通常不推荐进行脑部影像学检查。然而,随着能够有效治疗脑转移的系统性药物的出现,这一诊疗标准有可能会得到调整。如果患者一般状况差且预后不良,建议进行姑息治疗或针对靶病灶的治疗;对于一般状况良好且预后良好的患者,可以进行局部和系统治疗。局部治疗主要包括放疗和手术,可以在系统治疗之前或之后进行。对于系统治疗,当脑转移稳定时,可以根据初始脑转移速率(IBMV)评分制定治疗策略;对于活动性脑转移,有基于TKI的治疗方案,如图卡替尼或奈拉替尼;有基于ADC类方案,T-DXd或T-DM1;以及其他治疗方法,如卡培他滨单药或与图卡替尼联合使用。HER2CLIMB-02研究中,T-DM1+图卡替尼的方案在总人群以及基线脑转移患者中都实现了PFS获益,因此ADC+TKI的组合未来也可能成为脑转移患者可选方案。
另外,要注意立体定向放疗后发生放射性坏死的可能,同时使用放疗和ADC可能会增加这一风险。软脑膜的转移病变的治疗仍然是临床治疗的难点。
The incidence of brain metastasis in HER2+MBC increases with the duration of the patient's therapeutic line. The standard of care is not to perform brain imaging in asymptomatic patients, but this may change with the availability of systemic therapies with efficacy for brain metastases. If the patient's general condition is poor and the prognosis is considered poor, it is recommended to undergo palliative treatment or target lesion treatment; for patients in good general condition and good prognosis, local and systemic treatment could be performed. Local treatment mainly includes radiotherapy and surgery, which could be performed before or after systemic treatment. For systemic treatment, when brain metastases are stable, treatment strategies could be formulated with reference to the initial brain metastasis velocity (IBMV) score; for active brain metastases, there are TKI-based therapies like tucatinib or neratinib, ADC-based T-DXd or T-DM1, and other treatments such as capecitabine alone or in combination with tucatinib. Pay attention to the possibility of radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiotherapy. The use of ADCs simultaneously may increase that risk. The treatment of leptomeningeal metastases disease remains a clinical difficulty.
HER2+的MBC脑转移,一线治疗推荐紫杉醇联合帕妥珠单抗+曲妥珠单抗;二线治疗为T-DXd或图卡替尼/卡培他滨/ 曲妥珠单抗;三线有ADC和TKI等,是单独还是联合使用,建议根据每个患者的临床特征、风险评估等综合考虑后决定。另外,很多新的药物和治疗方法也都在研究探索中,比如ZW25、脑渗透性TKI ZN-A-1041以及HER2 Car T 细胞疗法等。
For HER2+ MBC brain metastases, the first-line therapy is recommended to be taxane combined with pertuzumab + trastuzumab (which may soon be replaced by T-DXd); the second-line treatment is T-DXd or tucatinib/CAPE/trastuzumab ; The third line includes ADCs and TKIs. Whether to use them alone or in combination, will be decided case by case, which depends on comprehensive consideration of each patient's clinical characteristics, risk assessment, etc.
讨论环节
Discussion
患者已在新辅助治疗或辅助治疗中接受过曲妥珠单抗和帕妥珠单抗,该如何选择一线治疗?
If patients have received trastuzumab and pertuzumab in neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment, how to choose the first-line therapy?
Hurvitz教授对已经接受过基于紫杉醇,及曲妥珠单抗和帕妥珠单抗治疗后进展或复发的患者,建议选择T-DXd为一线治疗方案;通常使用12个月无病间隔期来判断患者是否耐药。当发生T-DXd耐药时,首要考虑耐药机制,并考虑使用作用机制不同的化疗药物,或者TKI。
Pro. Hurvitz: For patient whose disease progresses or recurs after curative therapy with taxane based plus trastuzumab, pertuzumab based therapy, could use T-DXd as first line setting. Generally using a twelve months disease free interval to select whether the patients are resistant to the study drug. When resistance has developed to T-DXd, we have to think about mechanisms of resistance, and consider using chemotherapy with a different mechanism of action, or TKI.
DESTINY Breast -11研究中T-DXd单药队列已经完成了治疗,新辅助治疗中T-DXd单药是否足够,是否需要联合THP治疗?
李俊杰教授对T-DXd作为单药进行新辅助治疗有保留观点,Hurvitz教授介绍她本人的研究中心也在进行一项针对HER2低表达、HR+的乳腺癌,以T-DXd为新辅助治疗的临床研究(不与标准治疗对比),他们也认为单独使用T-DXd并不足够,可能需要增加紫杉醇,以达到治愈的目的。
Pro. Junjie Li has concern for using T-DXd as a single agent for neoadjuvant therapy. Pro. Hurvitz introduced that they started one new trial, which was looking at T-DXd as the neoadjuvant setting for HER2 low and HR+ breast cancer. It’s not compared to standard care, their concern is also T-DXd single agent may not enough for patient in the curative setting, may need taxane for very effective therapies.
对发生脑转移的患者,血脑屏障是否还存在, 是否可以用这个屏障来衡量TKI和抗体的疗效?
Does the blood-brain barrier still exist for patients with brain metastasis? Can this barrier be used to measure the efficacy of TKIs and antibodies treatment?
Hurvitz教授认为对脑转移患者其血脑屏障是否存在一直是有争议的,也需要重新思考之前关于血脑屏障的假设。现在有些临床研究在系统用药后检测血液和脑积液中的的药物浓度等来研究这个问题。
宋传贵教授也赞同可先建立肿瘤脑转移的动物模型来分析。
Pro. Hurvitz :There is a lot of controversy about blood brain barrier exists or not for the tumor brain barrier. We are beginning to rethink our assumptions about the blood brain barrier. There are some clinical trials to measure drug concentration in the plasma and CSF after systemic treatment. Pro. Chuangui Song is also agree to build animal models of brain metastasis to study it firstly.
活动性脑转移的治疗最佳模式是怎样的?
What is the best treatment model for active brain metastases?
袁渊教授的经验是对脑转移稳定的患者,先进行系统治疗,后续进行局部放疗或手术治疗,对活动性脑转移倾向于先做局部治疗。
Pro. YuanYuan introduced their experience, for patients with stable brain metastases, should receive systemic treatment first, followed by local radiotherapy or surgery; for patients with active brain metastases, local treatment is preferred firstly.
Hurvitz教授对活动性脑转移患者的治疗策略是,如没有发生脑占位症状,则进行系统性治疗;对病灶大于2cm的患者,首要进行局部治疗。非常重要的是可进行随机对照研究,比较先行放疗和先行系统治疗的优劣。在没有这些数据的情况下,按患者的临床特征来判断哪项治疗对患者更紧迫有效。
Pro. Hurvitz shared their treatment strategy:we are beginning to think about using systemic therapy even for patients with active brain metastases if they are not having mass effect. When the lesions are more than 2 cm, it should be treated locally first. What we really need are randomized studies comparing radiation first versus systemic therapy first to see how patients do. In absence of having that data, we use these clinical features to gauge how urgent it is to get response.
晁腾飞教授看好ADC联合抗血管类药物对脑转移患者的治疗可行性,并有临床研究在进行中。
Pro. Tengfei Cao is looking for the feasibility of ADC combined with anti-vascular drugs in the treatment for patients with brain metastasis, and they are beginning one clinical trial for this combination.
Hurvitz教授表示目前没有ADC联合抗血管类药物研究的数据,但是这种联合有助于治疗放射性坏死,甚至有助于将治疗药物输送至大脑。所以非常期待有这样的临床研究进行。
Pro. Hurvitz liked this idea, they don’t have the data for it, but it may help with radiation necrosis and even with delivery of the therapies to the brain. She would love to see this tested in clinical trial.
脑转移病灶稳定时,局部放疗和手术治疗是否必需?
When brain metastases are stable, if local radiotherapy and surgery are necessary?
Hurvitz教授建议在脑转移稳定时,如全身情况也稳定,不增加局部治疗,继续系统性治疗。临床上碰到的难题是患者脑外病灶稳定但脑转移病灶有进展,是否要继续系统治疗及增加局部治疗?这需要按每个患者的症状、放疗和系统治疗等具体情况来决定。
Pro. Hurvitz recommended:if the patient brain metastases are stable, and the disease outside of the brain is stable, the systemic therapy will be continued, not treated locally. When the patient with disease outside the brain is stable, but brain has some progress, this is the challenge, do we change the systemic therapy or continue the systemic therapy with the local therapy? This should be very individualised by patient’s symptoms, whether the patient had radiation before, and what systemic therapy they have had.
ADC类药物在HER2+MBC脑转移治疗的探索
李兴睿教授主持会议,重点交流ADC耐药的临床难点。由晁腾飞教授介绍了ADC类药物的现状,提出在出现ADC耐药后,基于耐药机制可能的治疗策略有:1. 换非ADC类(TKI或化疗),目前的研究结果显示有PFS延长,暂未有OS获益;2. 使用同靶点但不同载药的ADC药物序贯治疗,数个临床研究结果显示可降低耐药率,提高中位PFS,部分有OS获益;3. 不同靶点ADC药物的接力治疗。
对ADC类未来的发展前景,考虑如下:1.ADC与其他单抗、TKI、ICI等强强联合,如华中科技大学同济医院在进行中的ADC联合贝伐珠单抗治疗HER2+MBC脑转移的II期临床研究;2. ADC的自我革新,如探索抗体偶联的新模式,双特异抗体的ADC等;3. ADC类进入早期BC治疗,以减少复发。

讨论环节
李俊杰教授非常认可华中科技大学同济医院设计开展的ADC联合贝伐珠单抗治疗HER2+MBC脑转移的临床研究,给其他解决临床问题的研究提供了思路;并认为ADC类双抗会是未来的发展方向,但需要关注药物的安全性。
宋传贵教授发言表示TKI药物如吡咯替尼,和ADC类,单独或联合使用,如何联合,特别是对临床上难治性乳腺癌,如HER2低表达和三阴性乳腺癌的治疗,均是以后的研究方向。
袁渊教授分享,ADC耐药后,暂时还没有标准治疗方案。他们的治疗策略是选择既往未使用过的药物;对HER2+的MBC,因为没有确认的OS获益,在没有进一步循证医学数据支持的情况下,一般不使用ADC联合TKI,而且如联合使用,患者的消化道副反应会非常明显。
晁腾飞教授强调,早期BC和晚期BC的治疗策略不同,早期着重治愈患者,晚期旨在延长患者寿命并提高生活质量,要以患者最大获益的情况下,实行个体化治疗。
邱鹏飞教授考虑:在BC患者早期加入ADC类治疗,期望可以达到更高的病理缓解率,以达到外科手术降级治疗的目的。
杜雅莹医生介绍多肽偶联药物(PDC)药理学等信息,PDC更易于穿透血脑屏障,其筛选已趋成熟,且部分已商业化;PDC的靶向性可能低于ADC,但是免疫原性也低于ADC;目前的难点是PDC的偶联。
总结
李兴睿教授总结道,PDC的研发值得期待;此外,开展新的ADC/TKI的III期临床研究很难,需要在理解药物的特性、作用机制、如何配伍、安全性如何等的基础上进行,才有可能实行实验室研究项目的临床转化。期待更多新的临床研究可落地,更多的研究数据支持以解决临床的治疗难点。
排版编辑:肿瘤资讯-Awa











 苏公网安备32059002004080号
苏公网安备32059002004080号


